Glossary
Alternating current (AC) charging is typically how people charge their electric vehicles overnight. AC charging uses a lower voltage, either Level 1 (120 volts or normal household current) or Level 2 (240 volts or the equivalent power of an electric dryer). Though the low voltage levels mean a slower charge, AC charging can be easily installed in most households. It’s a great solution for residential, workplace, multi-unit dwellings, and other longer-term parking locations like hotels and municipal or airport parking garages.
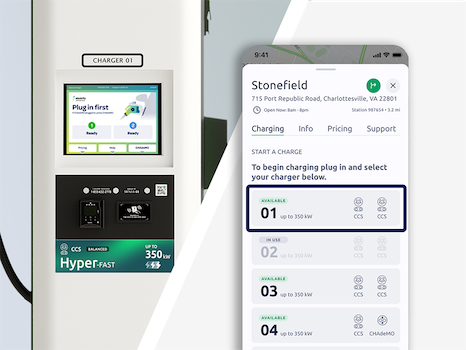
At Electrify America stations, the word “Balanced” may appear on a charger’s label or on the charger’s screen. Balanced chargers are typically located side-by-side and share a power cabinet, which supplies up to 350 kW across both chargers.
When a charger is Balanced, it can supply Ultra-Fast speeds up to 150 kW for vehicles capable of accepting this much power and can provide Hyper-Fast speeds up to 350 kW to capable vehicles when the adjacent charger is unused.
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) is a type of electric vehicle. BEVs store energy within the batteries inside the vehicle. A BEV does not have an internal combustion engine, but relies solely on an electric battery system for energy. It must be plugged into a charging source to replenish its battery. As of 2018, many BEVs can operate between 100 and 300 miles on a single charge.
CCS is a direct current (DC) fast charging protocol that is Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) certified, and is featured on vehicles produced by European and American car companies. The “combined” term in the CCS name designates its capability to incorporate the Level 2 (J1772™ standard) plug and DC fast charging connector into the same larger plug. The CCS plug nozzle is also commonly referred to as a “Combo plug.” You’ll have to find out from your car’s manufacturer whether your vehicle is compatible with a CCS or CHAdeMO plug. All Electrify America stations offer both CCS and CHAdeMO connectors.
CHAdeMO is a DC fast charging protocol that was first developed for the Japanese EV market; in the US, it is currently capable of charging vehicles like the Nissan Leaf and Mitsubishi iMiEV. The CHAdeMO protocol is officially recognized as an international DC charging standard by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) alongside CCS plugs for US and Europe, and the Chinese GB/T plug. All Electrify America stations offer both CHAdeMO and CCS chargers.
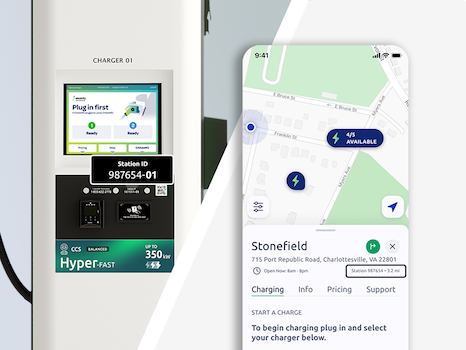
Each Electrify America charger is identified by a Charger ID, which can be found on the charger, the charger’s screen, and in the Electrify America app.
“Refueling” an electric vehicle battery with electricity. The time a battery takes to charge depends on the size of the battery in kWh and the amount of electric current being supplied.
Direct current is an electric current of constant direction. Electrify America fast charging stations all support DC.
Direct current (DC) charging for electric vehicles allows for higher charging speeds, since DC can be supplied directly to the electric vehicle’s battery at power levels normally higher than AC charging. The higher the DC power supplied, the faster the electric vehicle can be charged—provided the EV is designed to handle such power. Charging will slow down toward the end of your session in order to preserve your vehicle’s battery. This typically happens around 80% full, but is dependent on the model of your EV.
By 2019, it is expected that 150 kW+ DC fast charging will be available on a number of vehicles.
To illustrate the charging power difference between AC and DC fast charging, a Level 2, 7.2 kW AC charger can take one hour to deliver about 27 miles of EV range. A 50 kW DC fast charger can deliver the same 27 miles of range in about 10 minutes.
A virtual “card” on smartphones that uses NFC (near-field communication) to communicate a member’s account information to the charger. This allows members to use their Electrify America account balance to pay for a charge by simply holding their phone near the charger’s contactless reader.
Tip
: The contactless reader is identified by the message, “Members: Tap here to pay with plan”.
An electric vehicle uses electric motors and motor controllers to power the vehicle instead of propulsion via an internal combustion engine. EVs store electricity in a battery that powers the vehicle’s wheels through an electric motor. Different types of EVs include the battery electric vehicle (BEV), the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), the hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), and the fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV).
Hyper-Fast is a descriptive term that indicates CCS connectors delivering up to 350 kW. Hyper-Fast CCS connectors are identified by green labels on Electrify America chargers.
Electrify America’s pricing policy includes a $0.40 per-minute idle fee starting ten minutes after your charging session is complete, if you have not unplugged and moved your vehicle. This feature is designed to encourage drivers to move their car after they’re done charging to make room for others who need to charge.
One of the most common connectors is the Level 2 J1772™. Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standard adopted in North America and Japan.
A unit of energy equivalent to the energy transferred or expended in one hour by one kilowatt of power. Electric car battery size is measured in kilowatt-hours, so think of it as the electric car’s equivalent of the size of an internal combustion vehicle’s gas tank.
OCPP is the standard developed to provide powerful, open, and interoperable communication between the different electric vehicle charging infrastructure companies, hardware, and networks. The Open Charge Alliance (OCA) is the global consortium of public and private EV infrastructure leaders that have come together to promote this standard.
A PHEV is a type of hybrid electric vehicle that combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a large battery that can be recharged by plugging into an electrical outlet—or in some cases, an electric vehicle charging station. Plug-in hybrids typically can run in at least two modes: “all-electric,” where the motor and battery provide all the car’s energy, and “hybrid,” where both electricity and gasoline are used.
This technology features the IEC/ISO 15118 standard to make paying for a charge easier. Following setting up an Electrify America account, and inputting a payment method, the charger can recognize capable vehicles and will automatically complete the charge’s payment. For capable vehicles, there’s no need for cards or apps at the station; simply plug-in and charge.
This new technology is now available for a growing number of Plug & Charge-capable vehicles, including the 2021 models of the Porsche Taycan and the Ford Mustang Mach-E. Electrify America is the first company to offer this service to automakers.
SOC is the equivalent of a fuel gauge for the battery pack in an EV. The units of SOC are percentage points, with 0% meaning no charge left and 100% meaning fully charged. If your car makes the information available, our charging stations will tell you the SOC of your vehicle as you charge.
Each Electrify America station is identified by a unique Station ID. This can be found on the charger, the charger’s screen, and in the Electrify America app.
Ultra-Fast is a descriptive term that indicates CCS connectors delivering up to 150 kW. Ultra-Fast CCS connectors are identified by teal labels on Electrify America chargers.
Under Appendix C of the Consent Decree regarding “Volkswagen ‘Clean Diesel’ Marketing, Sales Practices, and Products Liability Litigation,” the following three vehicle types are considered Zero Emission Vehicles:
Under Appendix C of the Consent Decree regarding “Volkswagen ‘Clean Diesel’ Marketing, Sales Practices, and Products Liability Litigation,” the following three vehicle types are considered Zero Emission Vehicles:
An on-road plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) with zero-emission range greater than 35 miles as measured on the federal Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (UDDS) in the case of passenger cars, light-duty vehicles, and light-duty trucks, and 10 miles as measured on the federal UDDS in the case of medium- and heavy-duty vehicles; or
An on-road heavy-duty vehicle with an electric-powered takeoff.3
3United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2.0L Partial Consent Decree.